A chemical compound derived from an acid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one –OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an –O– alkyl (alkoxy) group. Esters are also usually derived from carboxylic acids. It may also be obtained by reaction of acid anhydride or acid halides with alcohols or by the reaction of salts of carboxylic acids with alkyl halides.
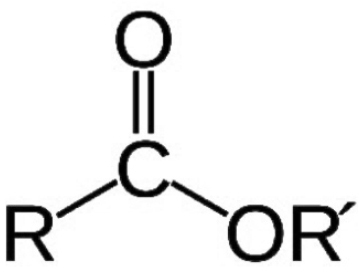
Ditallate esters of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) of various molecular weights. They are soluble in water, have low volatility, give very effective wetting, lubrication and emulsification. Ditallate PEG Esters are used in cleaners, lubricants, greases and metalworking fluids.
HLB: 12
pH1% 5.0 – 7.0
Appearance: Clear amber liquid
Acid Value: <5 mg KOH/g
Solids: >95%
Solubility: Water soluble
APPLICATIONS: Effective wetting and viscosity modifier. Emulsifier for oil in water emulsion and microemulsions.
Bring our expertise to your business. Let’s build valuable bonds together.